Ensuring electrical safety in your home is critical. This comprehensive guide provides an understanding of home electrical components for Indian home buyers. Knowing these basics will help you ask the right questions to your builder and ensure your home is electrically safe.
Importance
of Electrical Safety
Electricity,
while indispensable, is inherently dangerous due to its invisible nature. The
human body is a conductor of electricity, meaning contact can cause severe
injury or death. Ensuring electricity flows safely along intended paths is
crucial to avoid direct or indirect contact that could lead to accidents.
Direct
vs. Indirect Contact
- Direct Contact: Occurs when someone
accidentally touches a live wire, possibly due to current leakage or
exposed wiring.
- Indirect Contact: Involves contact with a
conductive part that has become live due to a fault, such as the metal
casing of an appliance.
Key
Components of Home Electrical Systems
Cables
and Wires
- Quality of Cables: Use high-quality, branded
cables for proper insulation and safety. Copper cables, adhering to IS
8130 standards, are preferred for their superior conductivity and safety.
Avoid aluminum wires.
- Single-Core vs. Multi-Core
Wires:
Single-core wires are commonly used for house wiring and should have
fire-retardant, low-smoke PVC insulation. Multi-core wires, which have
additional sheathing for enhanced safety, are used for connecting
appliances to plugs.
- Cable Sizes: Light and fan circuits
typically use 1.5 sq. mm cables, while power plugs generally use 4 sq. mm
cables for 6/16A outlets.
- Color Coding: Ensure the builder follows
standard color codes: RED, BLUE, YELLOW for phase wires, BLACK for
neutral, and GREEN for earth wires. This aids in safe maintenance and
repairs.
Cable
Joints
- Cable Connectors: Avoid joining cables by
twisting strands and insulating them with tape, as this is prone to risks
and hazards. Use cable connectors or heat-shrinkable sleeves with solder
for extra insulation.
Fuses and
MCBs
- Fuses: Provide protection from short
circuits and overloaded currents based on connected appliances and their
current usage. A blown fuse needs replacement, which can be inconvenient.
- MCBs (Miniature Circuit
Breakers): Offer
protection from short circuits and overloads. Standard sizes range from
1-4A/6A to 32A/40A. MCBs are available in Type B and Type C variants. Type
B is used for general appliances, while Type C is used for appliances with
motors.
RCCB/RCBO
- RCCB (Residual Current Circuit
Breaker):
Detects minute current leakages and cuts off electricity supply to prevent
shocks. Recommended sensitivity for household loads is 30 mA.
- RCBO (Residual Current Circuit
Breaker with Overcurrent Protection): Combines the functions of RCCB and MCB, providing
comprehensive protection against short circuits and current leakages.
Switches
and Sockets
- Quality: Opt for high-quality, branded
switches and sockets to ensure durability and safety. Poor-quality
switches can lead to heating and insulation failure over time.
- Safety Features: Switches should have thick,
long earth pins to prevent shocks. Sockets with shutters can prevent
children from inserting objects.
Mounting
Boxes
- Material: Use good quality Steel or GI
(Galvanized Iron) electrical boxes to aid in earthing and ensure proper
MCB tripping in case of faults.
- Installation: Proper installation ensures
durability and safety.
Conduits
- Concealed Wiring: Preferred for its safety and
aesthetics, as it reduces the risk of mechanical damage and smoke spread
during fires. Ensure the use of rigid or metallic pipes for exposed
wiring.
- Standards Compliance: Ensure conduits (whether
flexible or non-flexible) comply with Indian Standards for durability and
safety.
Earthing
- Importance of Earthing: Earthing is essential for
safety, acting as a "drainage" for leaking current. All
appliances must have proper earthing, and the earth wire should run
throughout the house. Earthing safeguards the premises from lightning and
earth fault situations and provides a low resistance path for fault
currents.
How
Earthing is Done in Residential Buildings
- Plate Earthing:
- GI or tinned copper earth wire
is bolted to a plate and buried at a depth of 3 meters or more, embedded
in alternative layers of coke and salts.
- The wire passes through a GI
pipe and is securely bolted to the earth plate.
- Water is poured into the GI
pipe to increase conductivity.
- The earth wire is connected to
the earth point of the socket and covered with soil.
By
understanding these essential components and their functions, home buyers can
better ensure that their homes are protected from electrical hazards, providing
peace of mind and safety for all occupants. This checklist serves as a guide to
ask the right questions and verify the quality and safety of the electrical
system in your new home.
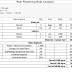
Checklist
Table for Home Electrical Components
|
Component |
Description |
Key
Points |
|
Cables
and Wires |
High-quality,
branded cables for insulation and safety. Prefer copper over aluminum wires. |
- Use
copper cables adhering to IS 8130 standards- Avoid aluminum wires- Use
fire-retardant, low-smoke PVC insulation for single-core- Multi-core wires
have extra sheathing for safety- Standard cable sizes: 1.5 sq. mm for
light/fan circuits, 4 sq. mm for 6/16A power plugs- Follow color codes: RED,
BLUE, YELLOW for phase, BLACK for neutral, GREEN for earth |
|
Cable
Joints |
Proper
methods for joining cables to ensure safety and reduce risks. |
- Use
cable connectors or heat-shrinkable sleeves with solder- Avoid twisting
strands and insulating with tape |
|
Fuses
and MCBs |
Protect
from short circuits and overloads. Fuses need replacement when blown; MCBs
(Miniature Circuit Breakers) offer reusable protection. |
- Standard
MCB sizes: 1-4A/6A to 32A/40A- Type B for general appliances, Type C for
motor appliances |
|
RCCB/RCBO |
Advanced
protection devices detecting minute current leakages and combining functions
of RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) and MCB. |
- RCCB
recommended sensitivity: 30 mA for households- RCBO combines RCCB and MCB for
comprehensive protection |
|
Switches
and Sockets |
High-quality,
branded switches and sockets with safety features to prevent shocks and
ensure durability. |
- Use
switches with thick, long earth pins- Opt for sockets with shutters to
prevent accidental contact by children |
|
Mounting
Boxes |
Steel or
GI (Galvanized Iron) electrical boxes that aid in earthing and ensure proper
MCB tripping in case of faults. |
- Ensure
high-quality, durable materials to prevent electrical hazards |
|
Conduits |
Concealed
wiring for safety and aesthetics, with conduits complying with Indian
Standards for durability. |
- Use
rigid or metallic pipes for exposed wiring- Concealed wiring reduces
mechanical damage and smoke spread |
|
Earthing |
Essential
for safety, acting as a "drainage" for leaking current and
safeguarding from lightning and earth faults. |
- Ensure
proper earthing for all appliances- Earth wire should run throughout the
house- Proper earthing techniques such as plate earthing using GI or copper
plates |






I called Matt Farrell Electrical for an emergency repair, and I was so impressed by how fast they responded. The technician diagnosed the issue immediately and had our power back up in no time. Professional, efficient, and affordable — exactly what you want in an electrical company!
ReplyDeleteReusable bottles and tumblers featuring minimal and modern art designs also promote environmentally conscious living. By replacing single-use plastic bottles and cups, they help reduce waste and minimize environmental impact. Their durable construction encourages long-term use, supporting sustainable habits. For today’s consumers, sustainability is a key aspect of thoughtful design, and art-inspired reusable drinkware embodies this commitment while combining style with responsibility.
ReplyDeletehttps://colornjoy.com/products/teddy-bear-coloring-water-bottle-outdoor-toys
https://colornjoy.com/products/rainbow-squad-coloring-water-bottle-cartoon-character
https://colornjoy.com/products/explorer-time-coloring-water-bottle-adventure-theme
https://colornjoy.com/products/cactus-oasis-coloring-water-bottle-flower-theme
https://colornjoy.com/products/cozy-ghost-halloween-40oz-tumbler-travel-mug