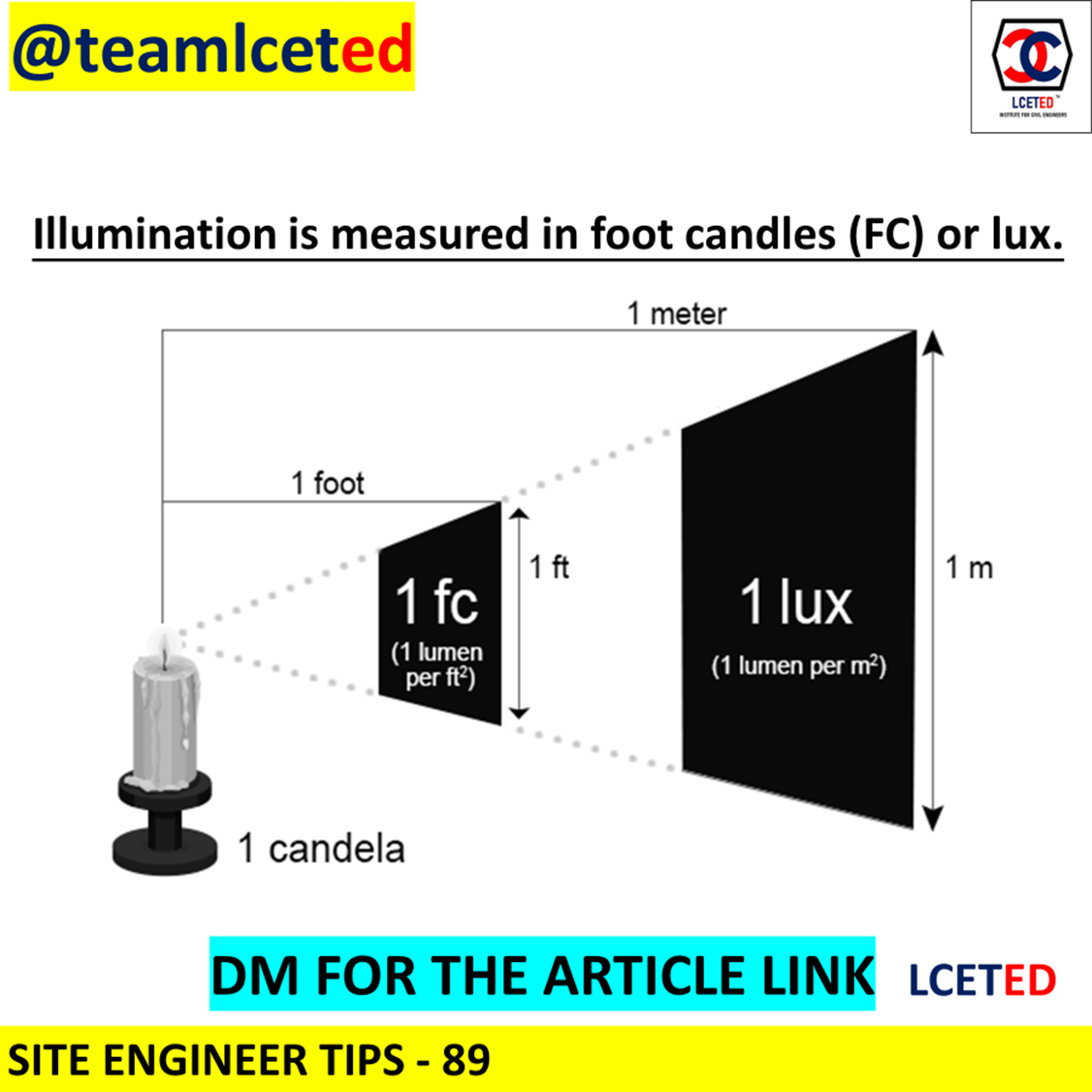
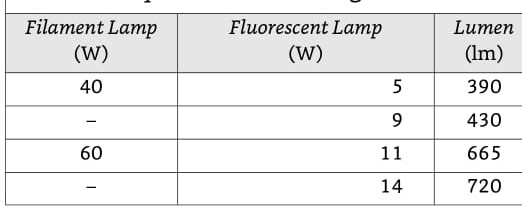
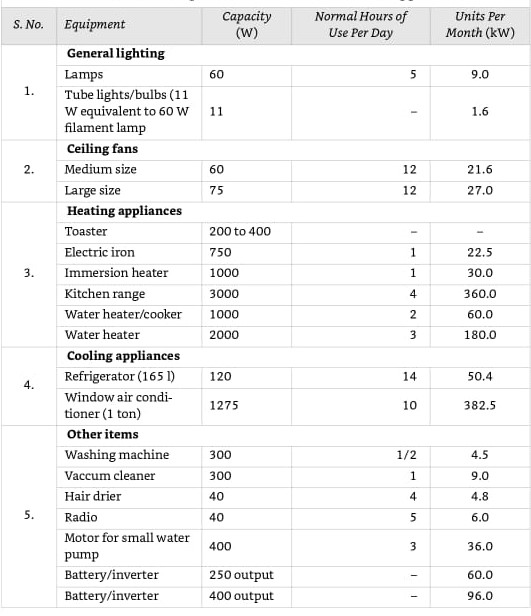
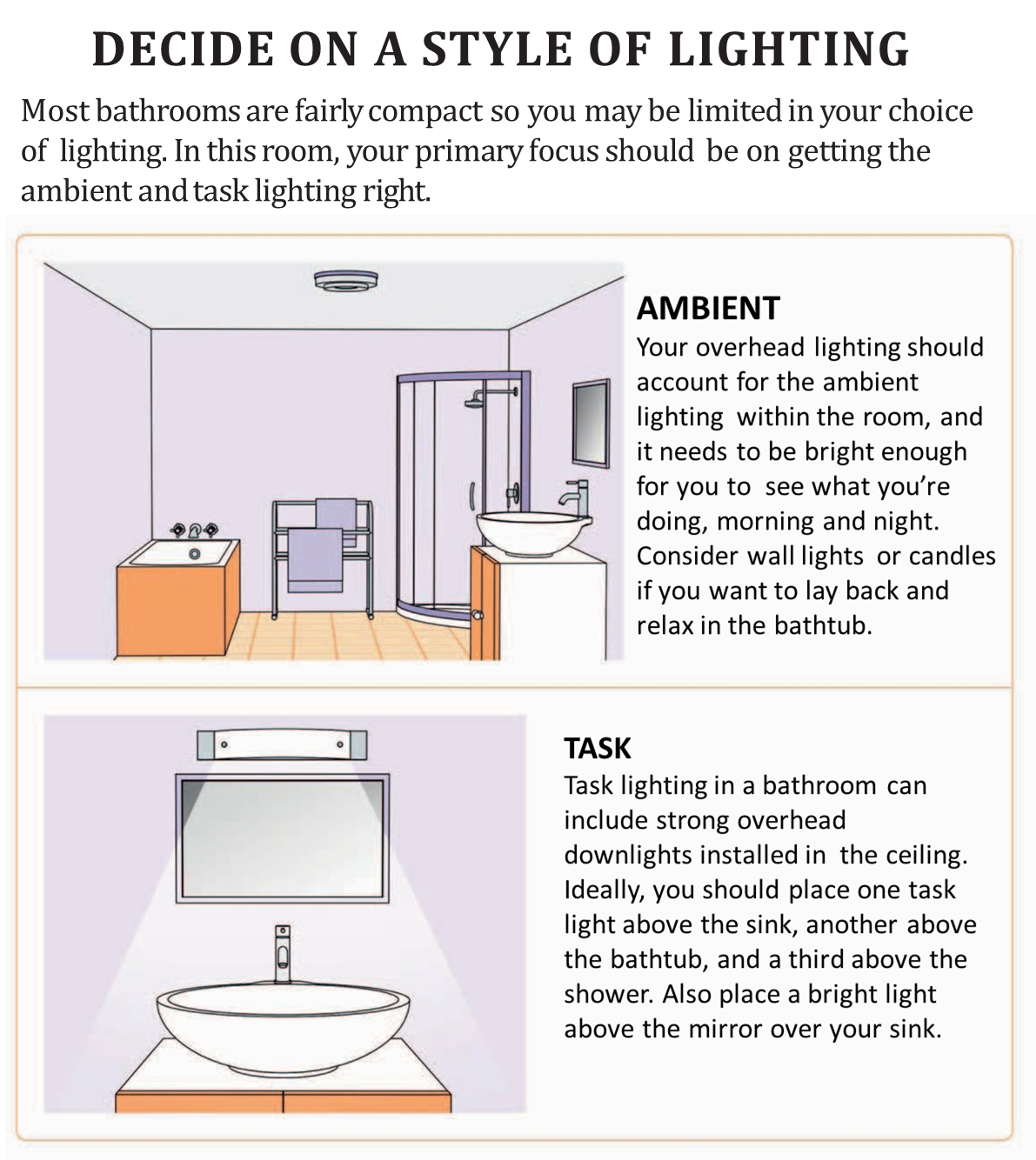
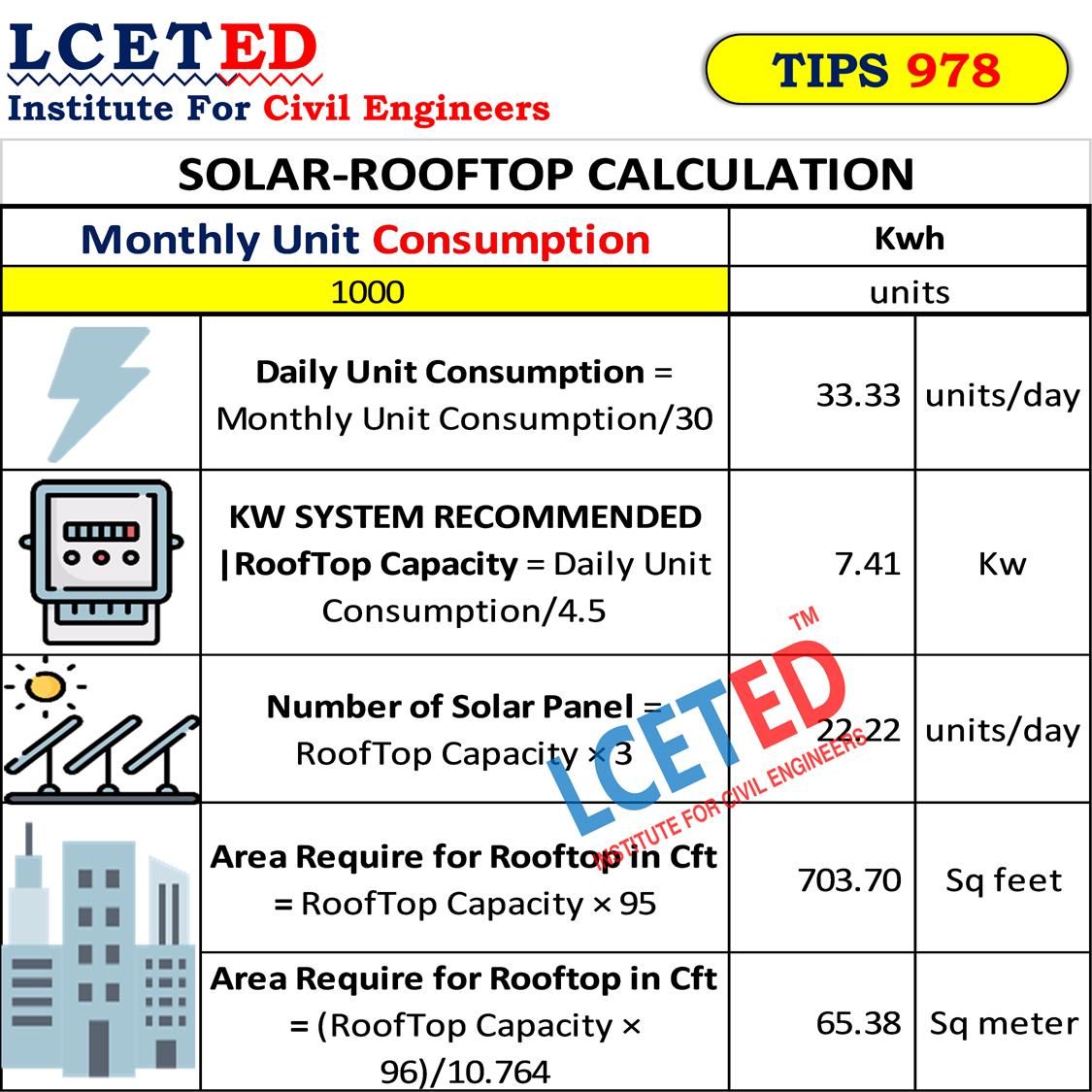
Ensuring electrical safety in your home is critical. This comprehensive guide provides an understanding of home electrical components for Indian home buyers. Knowing these basics will help you ask the right questions to your builder and ensure your home is electrically safe.
Importance
of Electrical Safety
Electricity,
while indispensable, is inherently dangerous due to its invisible nature. The
human body is a conductor of electricity, meaning contact can cause severe
injury or death. Ensuring electricity flows safely along intended paths is
crucial to avoid direct or indirect contact that could lead to accidents.